ECOSOC at 80: A Turning Point for Multilateralism and Global Cooperation
"Looks back and derives policy teachings on how to work together in the future". On 23 January 2026, the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) celebrated 80 years since its inception as provided in the UN Charter in 1945 and its first formal assembly in 1946. This anniversary would be a good time to look back at the historical legacy of the Council and to re-establish its relevance in creating an inclusive, resilient, and progressive multilateral system. Being one of the six key organs of the United Nations, ECOSOC was established in order to organize the economic, social, and cultural activities of the UN and facilitate international cooperation and development. Since its establishment, it has been at the centre stage of promoting the essence of the UN Charter, especially the promotion of higher standards of living, social progress, and provision of solutions to global economic and social needs and challenges through collective action.
During the last eight decades, ECOSOC has been a remarkable global venue uniting Member States, UN bodies, civil society, the business sector, higher education establishments, and the youth. Its work has been developing along with the global priorities that are post-war recovery and decolonization, up to solving such problems as climate change, expanding inequality, humanitarian emergencies, and sustainable development. ECOSOC has taken a leading role in the past few years in developing the 2030 Agenda on Sustainable Development, which helps in creating policy coherence at the economic, social, and environmental levels. The coordinating and convening role of ECOSOC in the UN system has also been reinforced in the past ten years as a result of institutional reform. The Council engages through its commissions, forums, and thematic segments in promoting dialogue, innovation, and consensus on the emerging global issues, and it also makes sure that follow-up is made to major international conferences and summits.
The 80th anniversary, the theme of which is a turning point of multilateralism, is also an era of global crises that are not resolvable by just a country. It also refers to the fact that solidarity, inclusiveness, and valid multilateral cooperation are imperative. With the UN system being challenged by complex issues in the 21st century, ECOSOC stands as a pillar in the international governance system, and it will continue to strengthen the need to address issues as a team to create a more just, sustainable, and peaceful world.
Latest News
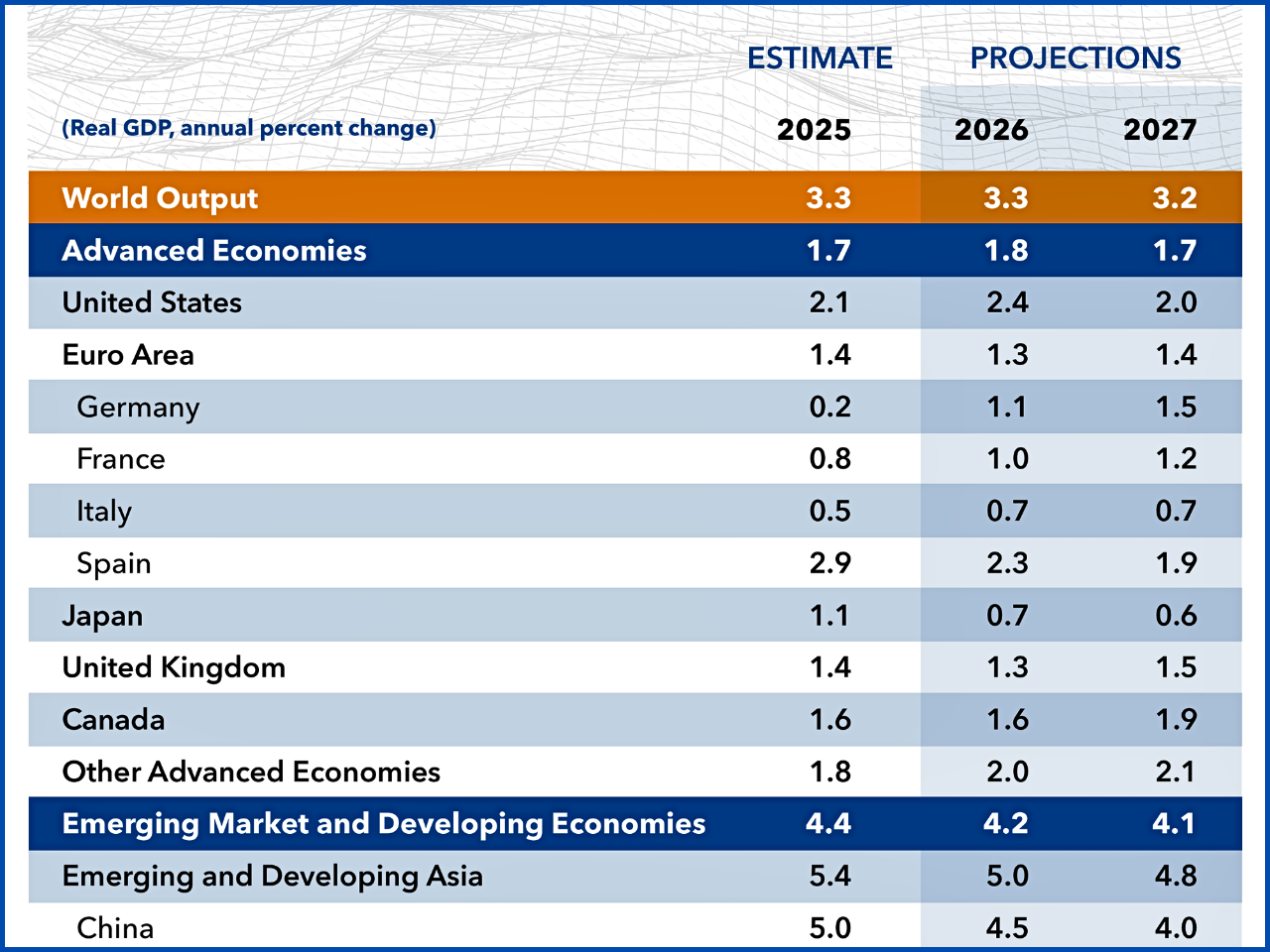
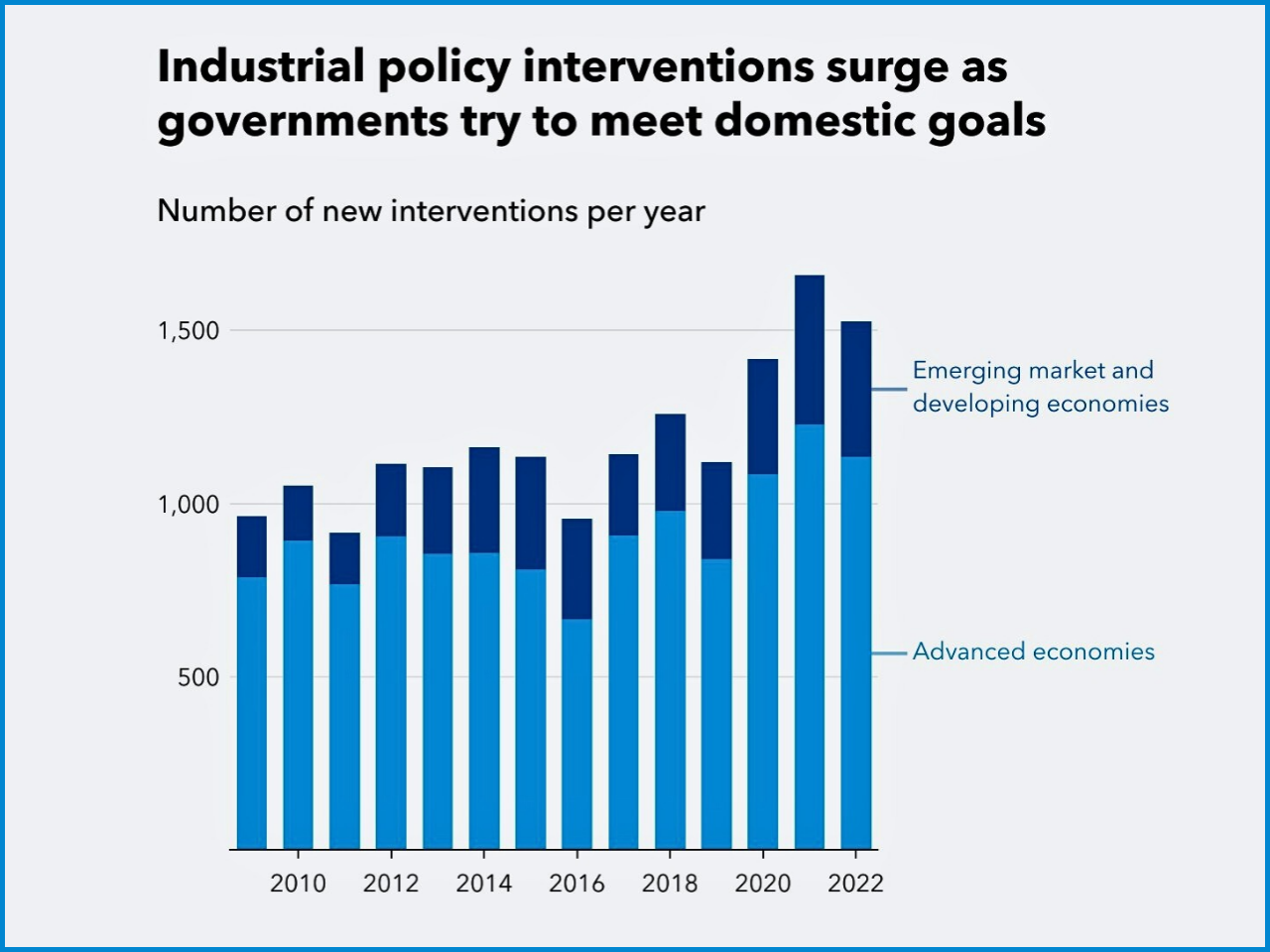
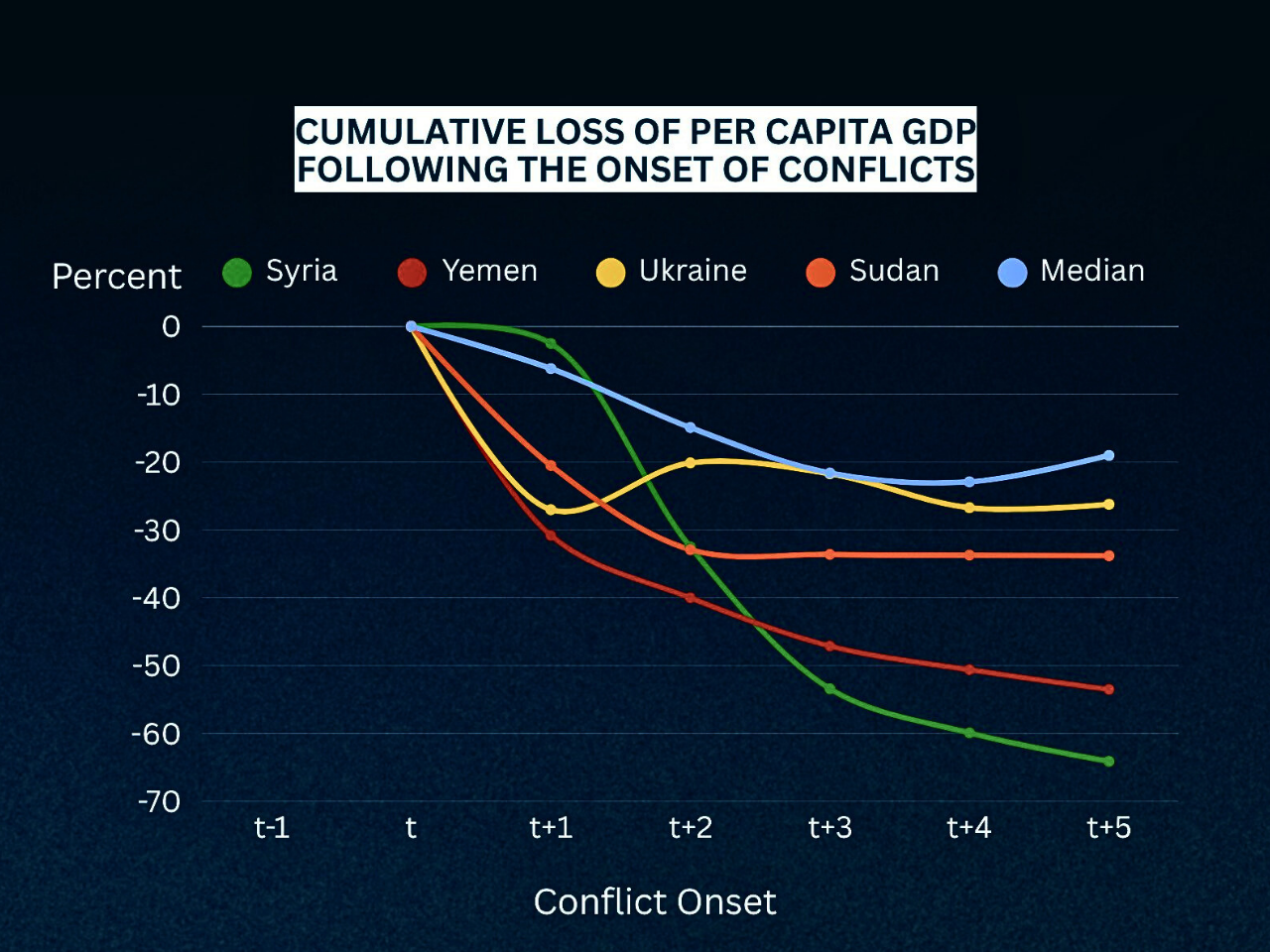
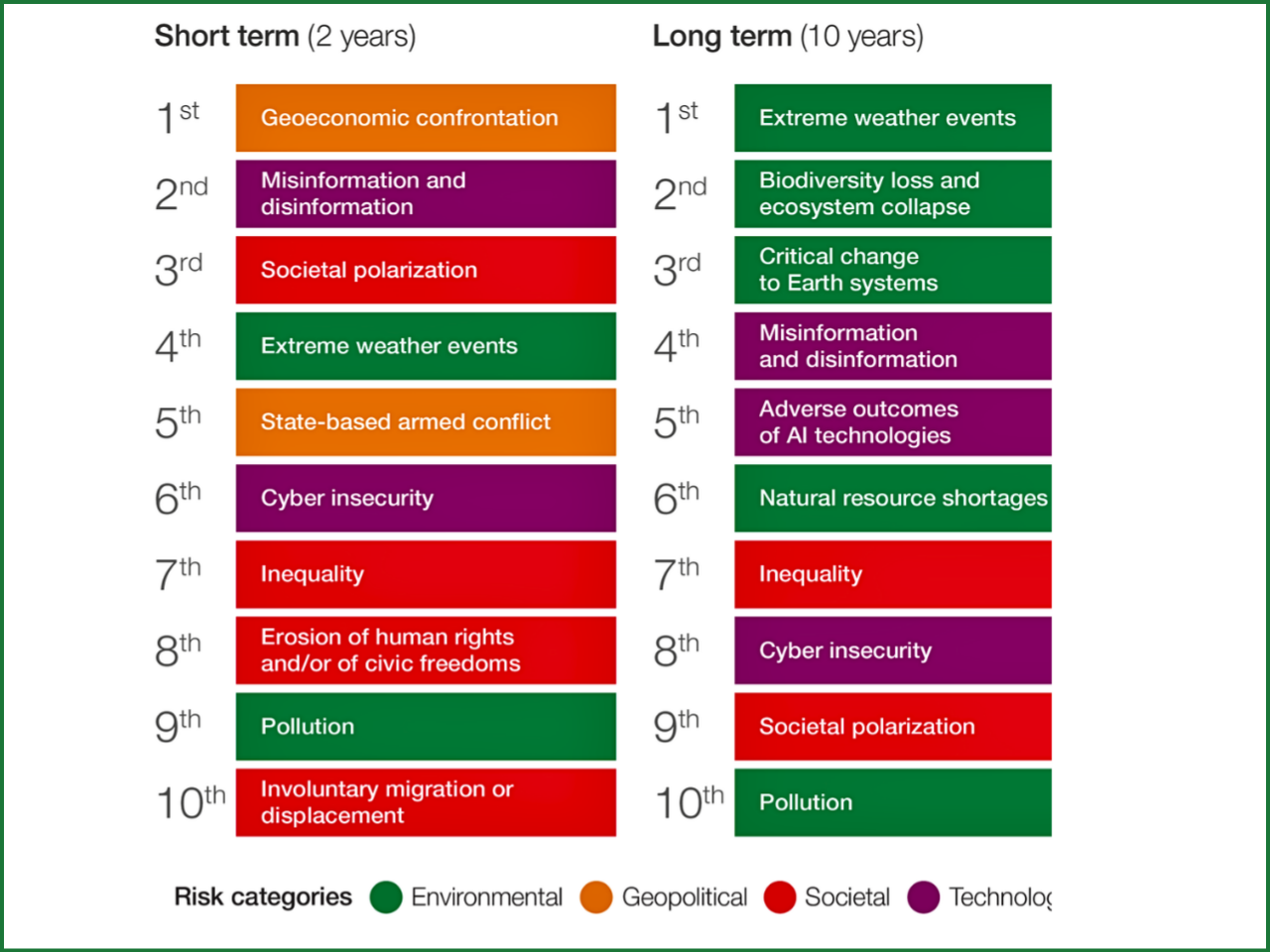
Global Risks Update 2026: Navigating an Age of Competition and Uncertainty
According to the World Economic Forum’s Global Risks Update 2026, we are moving into an “Age of Competition” with an increase in uncertainty, division between things, and crises that are intertwined or mutually influential. Drawing upon the opinions of 1,300 global leaders and experts, this report assesses risks both from 2026 to 2028 (the short-term) and 2036 (the long-term).
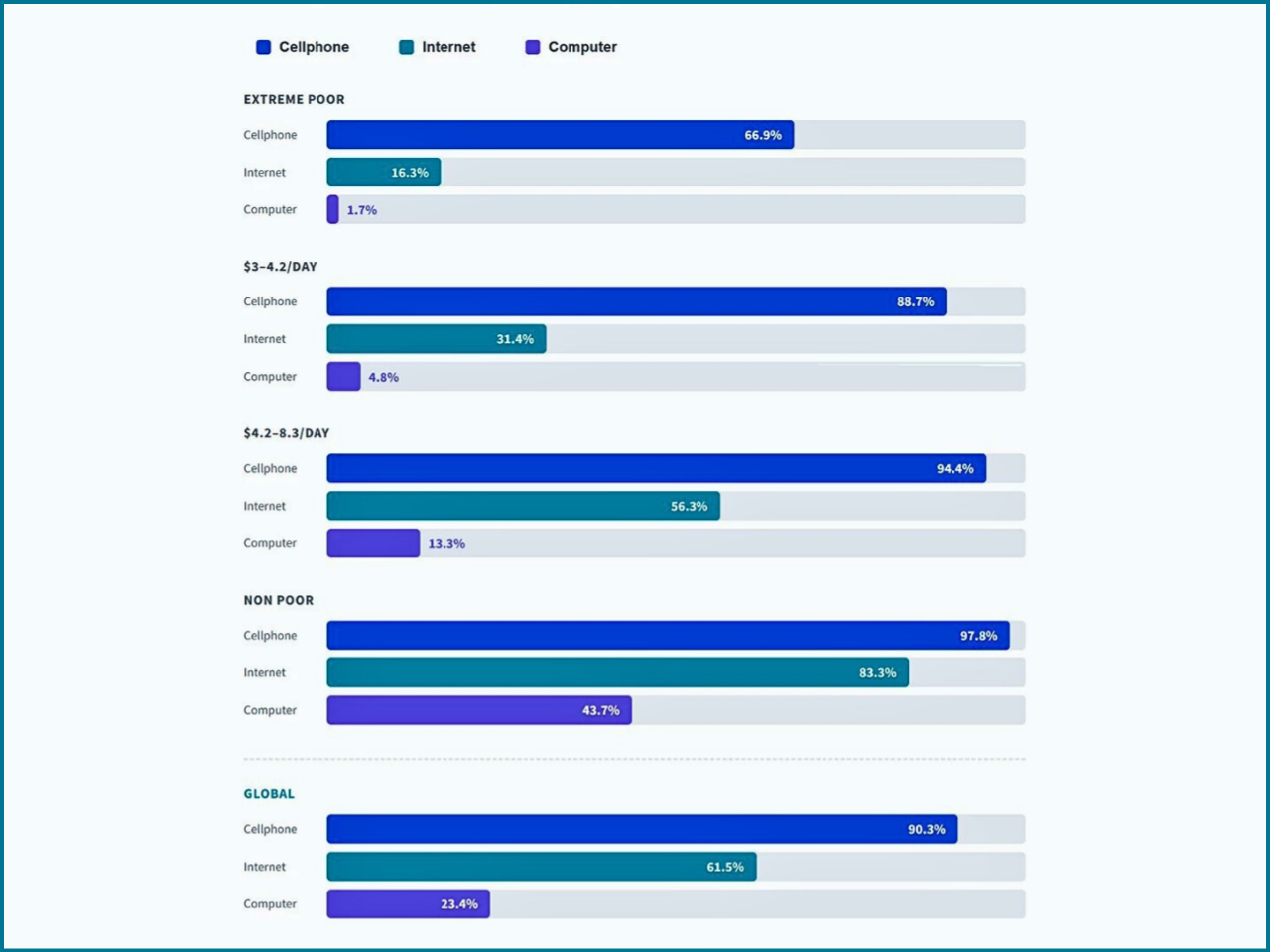
Bridging the Digital Divide: Unlocking Opportunities for the World's Poorest
The world's poorest people are still excluded from the opportunities available in a growing digital economy. Many poorer households [including those in the low or lower-middle class categories] continue to remain offline. Through being offline, these households will continue to be restricted from taking advantage of all the opportunities that digitalization provides.
Investing in Health: A Strategic Approach to Economic Growth and Job Creation
The research associated with the recent health agenda of the World Bank demonstrates that one vacancy in the health sector may result in the emergence of over three vacancies in the rest of the overall economy, such as pharmaceuticals, logistics, digital services, construction, and medical manufacturing, among others.

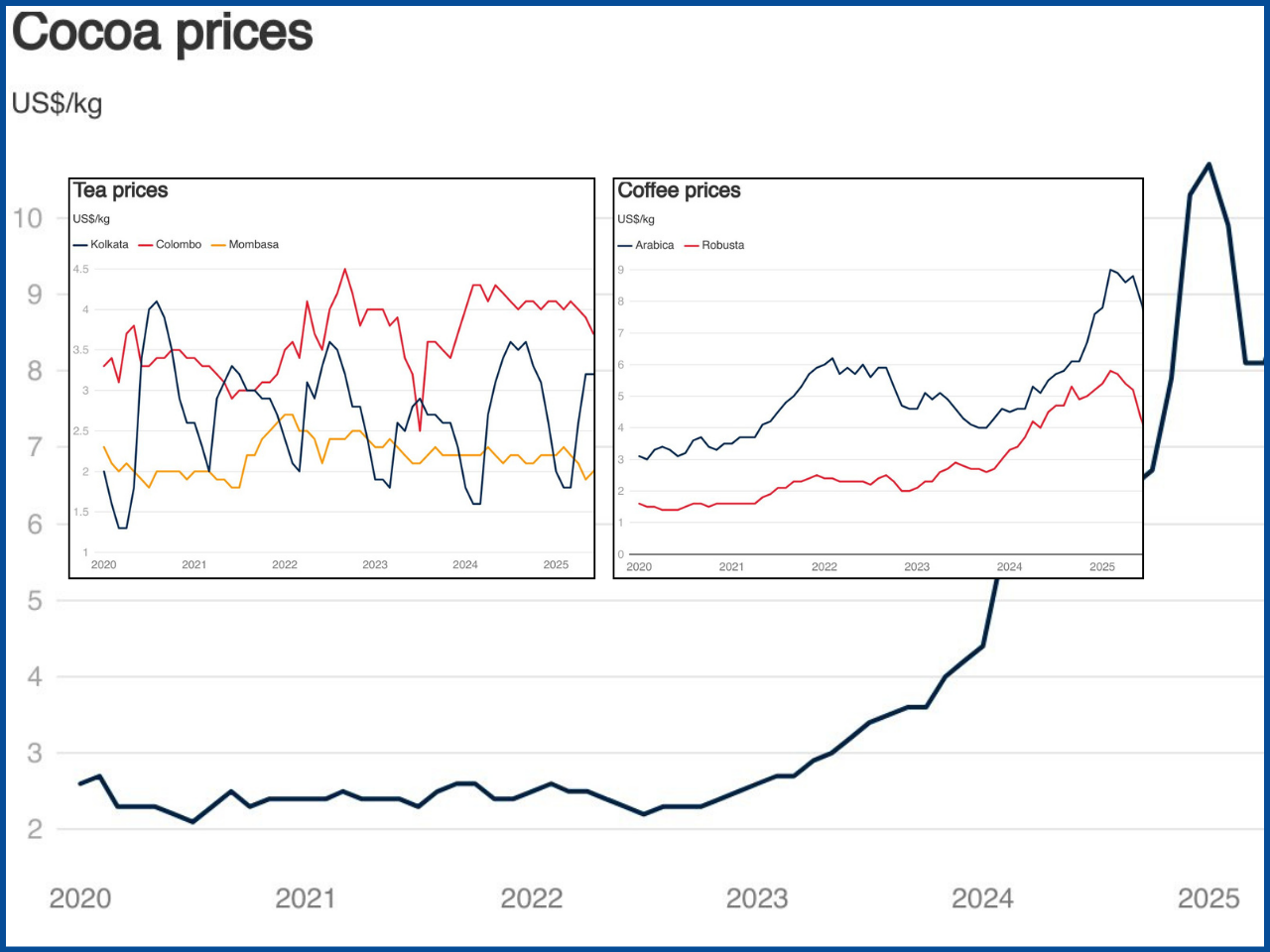
Global Beverage Prices Ease as Coffee and Cocoa Supplies Recover
In late 2025, the World Bank’s beverage price index decreased significantly after increasing drastically throughout 2025 (the coffee and cocoa prices have begun to fall) and as the tea prices remain stable for a significant period of time. Following the forecasted rise of the beverage price index by 18% for 2025, it is forecast to decline by 7% for 2026 and by another 5% for 2027 due to anticipated increases in output levels.
Free To Activate Membership