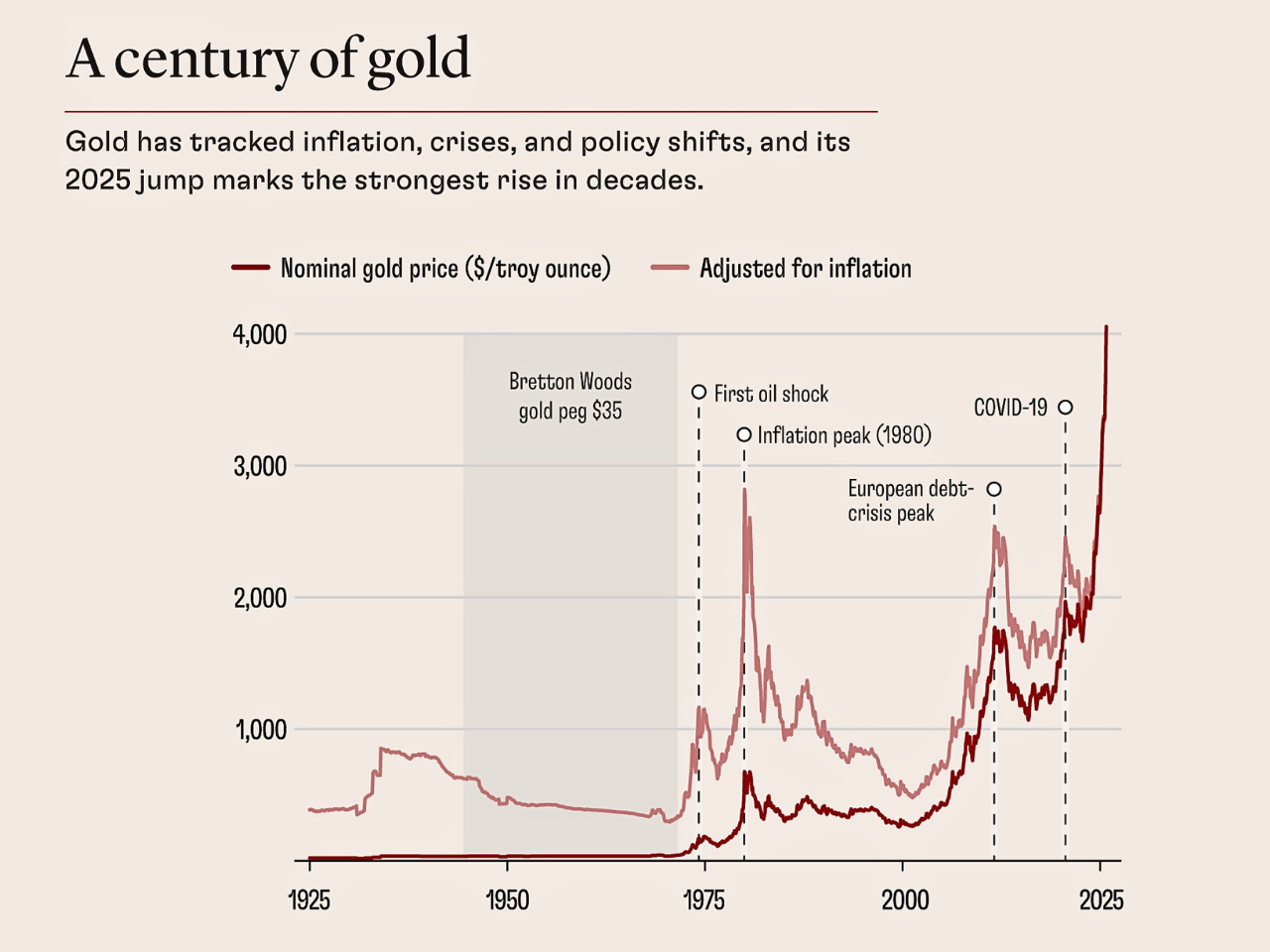
India's Economic Resilience: A Beacon of Hope in Turbulent Times
(Talk about how India handled its fiscal consolidation, spending on infrastructure, and macroeconomic stability according to best practices in the world) The Union Budget 2025-26 and the Economic Survey of India present a long-term economic plan that would enable the country to focus on internal development and make changes in the face of the unpredictable global world. The policy framework depicts a balance of fiscal discipline, structural reform, and increased involvement in international markets. According to the Economic Survey, the mid-term potential growth rate of India has risen to approximately 7 per cent, and this has been fueled by a consistent government investment, development of a rising network of infrastructure, and efficiency of logistics. This is a positive thinking that takes place at a time when the global economy is experiencing increased trade frictions, capricious capital movement, and declining investment rates. In spite of these external forces, India has still managed to exhibit resilience in terms of macroeconomic fundamentals and constant reform momentum. One of the main achievements of the Budget is the introduction of the National Mission on Manufacturing, whose purpose is to increase the manufacturing industry to 25 per cent of the GDP by 2035. The mission is also aimed at creating 143million jobs and growing the merchandise exports to USD 1.2 trillion. These plans are an indication that India aims to become closer to global value chains and to lessen reliance on external supply shocks.
In the investment front, the Survey reports that global foreign direct investment fell by 11 per cent in 2024, and India still received consistent inflows of foreign direct investment in the country because of policy stability and market potential. The latest trade and investment agreements, such as USD 100 billion through the India-EFTA partnership, shall result in an even greater leverage given to India as a favorable destination to invest in.
Sectoral trends are also positive. The growth in the agriculture and allied industries has been an average of 4.4 per cent in the last five years, with good contributions by livestock and fisheries. The growth of the financial sector has taken a new step with the International Financial Services Centre at GIFT City that currently accommodates more than a thousand international organizations and has a total of banking assets worth USD 100 billion and above. Generally, Budget 2025-26 has a policy roadmap that balances between domestic development priorities and global best practices. Through enforcing creativity, competitiveness in manufacturing, and financial prudence, India seeks to overcome the turbulence of the world while consolidating its position in the world economic development as a major energy source.
Latest News
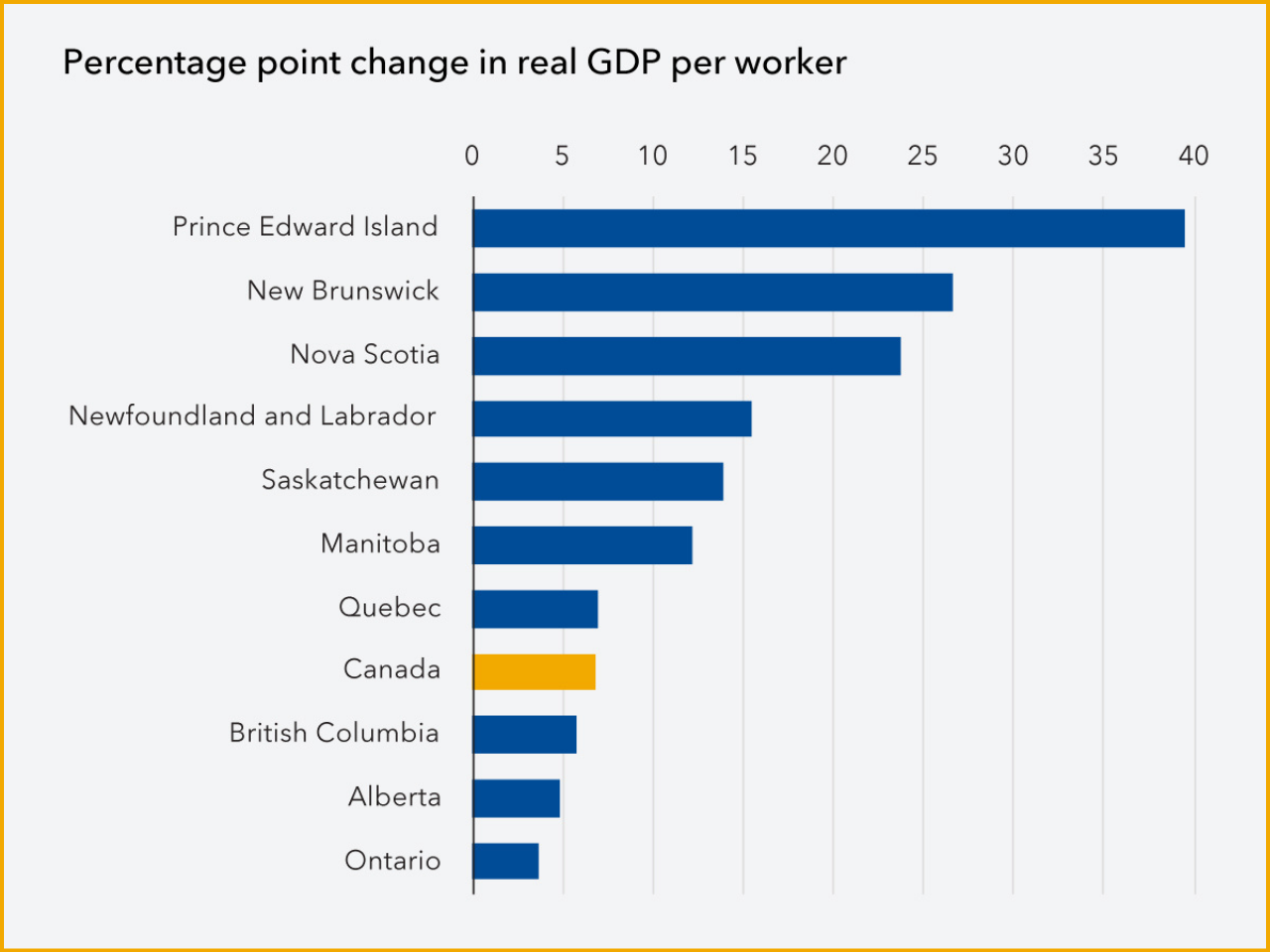
Breaking Down Barriers: How Canada Can Boost Productivity and Growth by Reducing Internal Trade Barriers
The Canada’s long-run real GDP would increase by an estimated 7%, representing an increase of approximately C$210 billion. Increasing the productivity of firms by removing these barriers would, in turn, stimulate economic development primarily through enhanced productivity, more efficient allocation of resources, increased competition among firms and improved firm growth versus demand increases in the short term.
EU Opens First Legal Gateway Office in India: A New Era for Talent Mobility and Trade
The long-awaited India-EU Free Trade Agreement (FTA) was finally signed, ending two decades of talks. European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen opined that the new office will serve as a single-stop shop to Indian students, professionals, researchers, and seasonal workers. The facility will unite visa data, mobility advice, and employer connections across Europe to streamline access to lawful migration routes and align with the labour-market needs and legal frameworks of specific EU member states.

Europe's Aging Population Meets Social Economy Solution: Care, Housing, and a New Era of Support
Europe is under the pressure of increasing ageing of its population, mounting care demand with a decreasing workforce, and escalating cost pressures. In the present day, caring is the reason behind almost one in every three Europeans, which highlights the burden on families, the labour market, and the welfare systems.

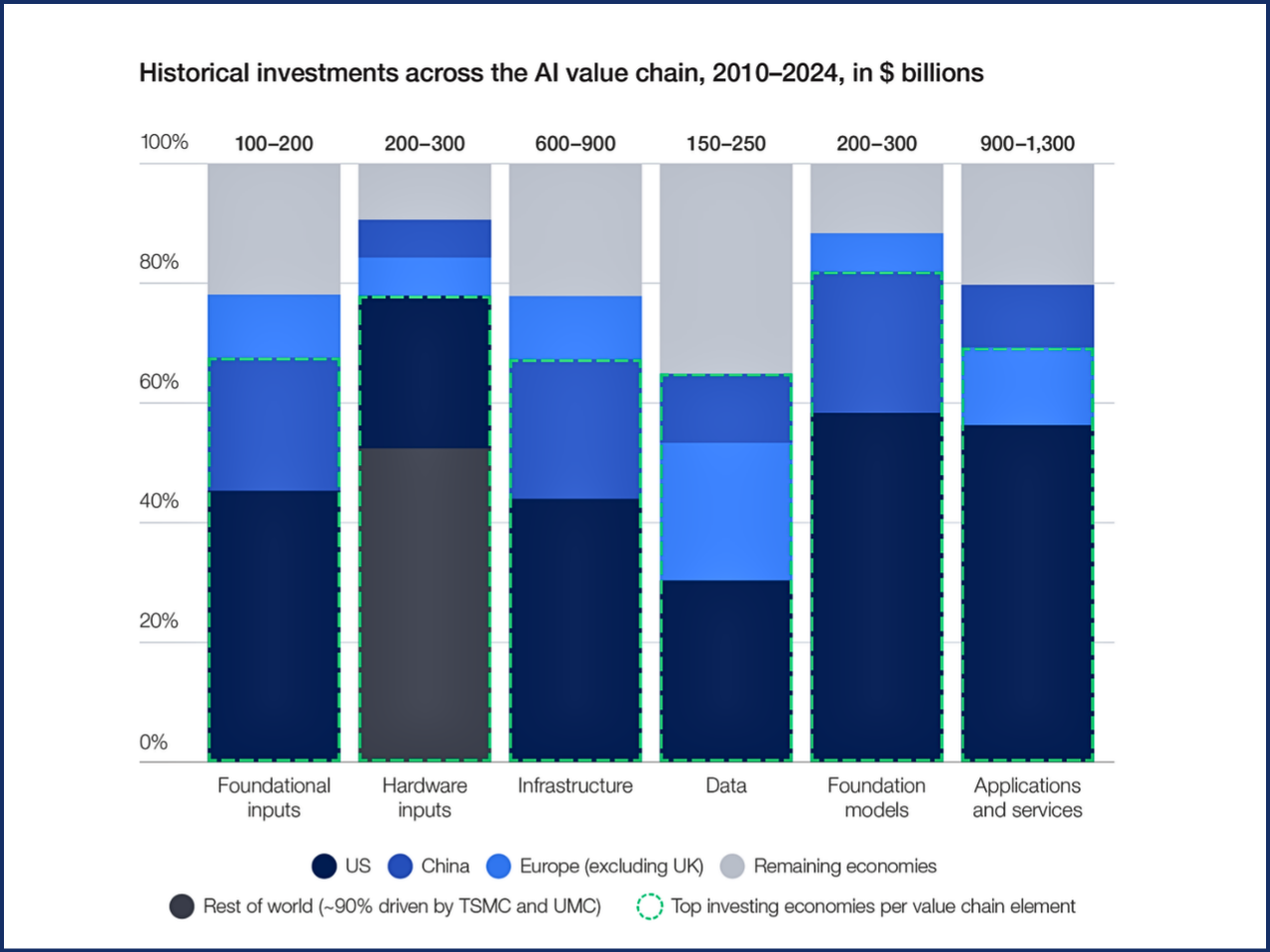
Rethinking AI Sovereignty: Why Strategic Interdependence is the Key to Global Competitiveness
The case that, rather than defining “AI Sovereignty” in terms of total self-sufficiency, a new framework based on the concept of strategic interdependence is more compatible with achieving success in an AI environment and will produce a competitive advantage for economies. Strategic interdependence focuses on encouraging collaboration based on comparative advantage (what an economy does well), interoperability between AI systems, and creating regional and global trusted partnerships.
Latest Podcast

Global Labor Market in Crisis: 2.1 Billion Workers in Informal Employment, 284 Million in Extreme Poverty
According to the Employment and Social Trends 2026 report from the International Labour Organisation, the world labor market has remained tough amid continued economic instability. While the global unemployment rate is predicted to stay very low at 4.9% in 2026, it is also expected to reach a record high of 4.9% by that year.
Free To Activate Membership